Plaque psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that affects millions of people, including a significant number of seniors. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and knowing the available treatments are crucial for managing this condition effectively. This article will provide a comprehensive overview of plaque psoriasis, including what it looks like, the challenges of severe scalp plaque psoriasis, and the latest treatments available.
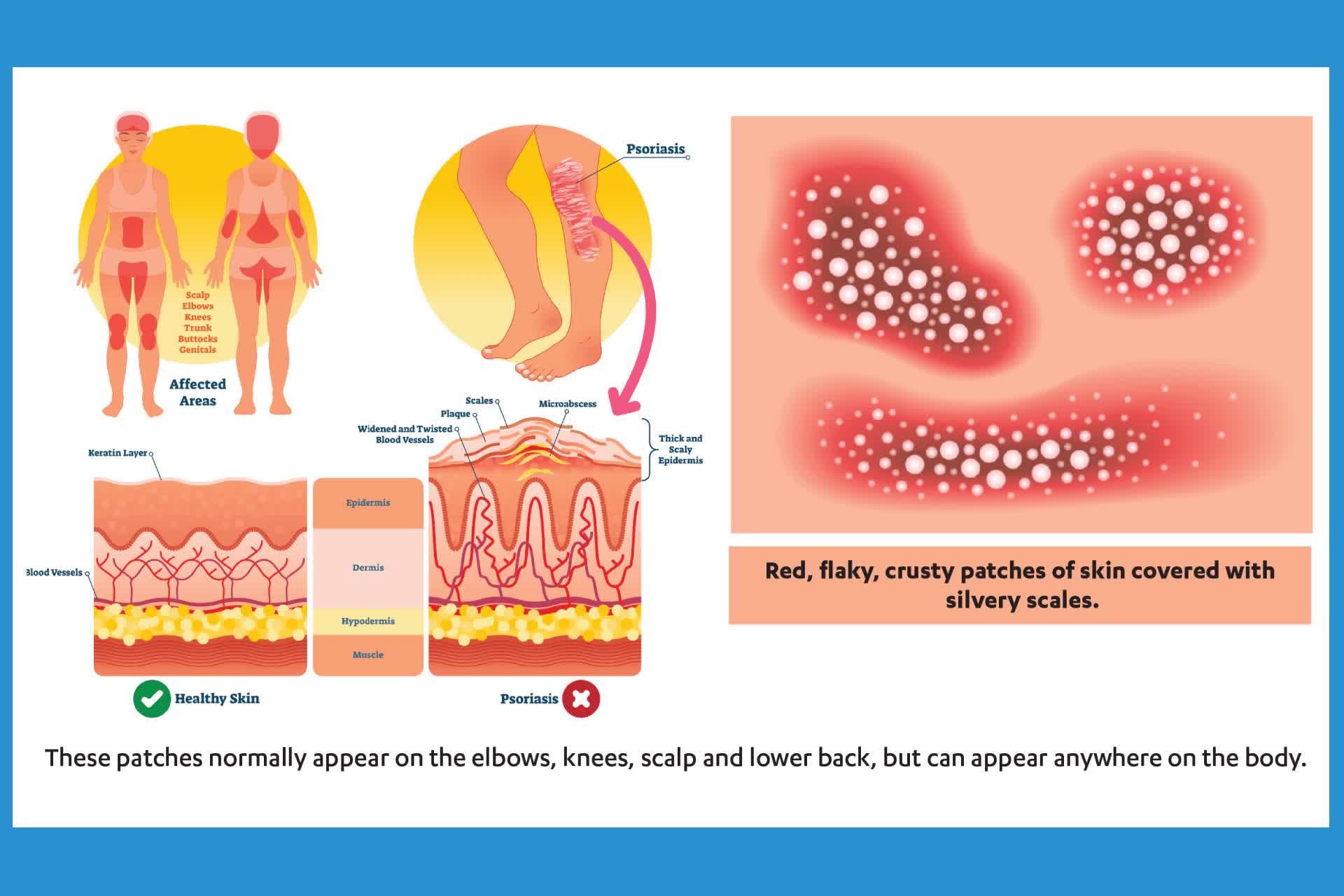
Plaque psoriasis is the most common form of psoriasis, characterized by raised, inflamed, red patches on the skin covered with silvery-white scales. These patches, or plaques, can appear anywhere on the body but are most commonly found on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back. The condition can range from mild, with small, localized patches, to severe, covering large areas of the body.
For seniors, understanding what plaque psoriasis looks like is the first step in recognizing the condition and seeking appropriate treatment. The plaques can be itchy, painful, and even crack and bleed, which can significantly impact daily life. In some cases, psoriasis can affect the nails, causing them to become thickened, pitted, or ridged.
Severe scalp plaque psoriasis is a particularly challenging form of the condition. It can extend beyond the hairline, affecting the forehead, neck, and around the ears. This can lead to discomfort, social embarrassment, and difficulty managing daily hair care routines.
The exact cause of plaque psoriasis is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to an immune system malfunction that triggers rapid skin cell production. In people with psoriasis, skin cells build up quickly on the surface, forming the characteristic scales and red patches.
Several factors can trigger or exacerbate plaque psoriasis, including:
Managing plaque psoriasis often requires a multifaceted approach, including topical treatments, phototherapy, and systemic medications. In recent years, new treatments for plaque psoriasis have emerged, offering hope for those who struggle with the condition.
Treatment Option | Description | Benefits for Seniors |
Topical Treatments | Includes corticosteroids and vitamin D analogs applied directly to the skin. | Easy to apply, directly targets affected areas, minimal systemic side effects. |
Phototherapy | Controlled exposure to ultraviolet light to reduce symptoms. | Non-invasive, can be performed in a clinical setting, effective for widespread psoriasis. |
Systemic Medications | Oral or injectable drugs that work throughout the body to control psoriasis symptoms. | Effective for severe cases, can significantly improve quality of life, but may require regular monitoring. |
Biologics | Target specific proteins in the immune system to reduce inflammation. | High efficacy in reducing symptoms, newer drugs with promising results, may be suitable for those who don't respond to other treatments. |
Severe scalp plaque psoriasis requires special care and attention. The scalp is a challenging area to treat due to the presence of hair, which can make applying treatments difficult. However, several approaches can help manage this condition effectively:
Plaque psoriasis, particularly in its severe forms such as severe scalp plaque psoriasis, can be a challenging condition to manage, especially for seniors. However, understanding what plaque psoriasis looks like and being aware of the new treatment options for plaque psoriasis can significantly improve the quality of life for those affected. By staying informed and working closely with healthcare providers, seniors can find effective ways to manage their condition and maintain a comfortable and fulfilling life.
Editor’s Picks




Related Articles